Process Vessel Reference Electrode
The Model FE Process Vessel Reference Electrode is designed to operate in environments where ordinary reference electrodes cannot survive. These include elevated temperatures, high pressures and/or contaminated electrolytes. This is a two-piece unit consisting of a bridge which is permanently installed at each location where potential readings are desired and a separate reference electrode. Because the reference electrode is a separate piece, it is isolated it from the aggressive environment which substantially increases its service life. The reference electrode can also be removed for calibration or service without affecting the integrity of the vessel.
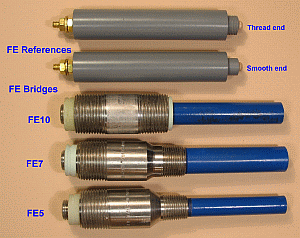
The Model FE10 bridge has a 316L stainless steel nipple which threads into a 1 in. NPT hole. Variations of this design have been developed which thread into a 3/4 inch NPT (Model FE7) or a 1/2 inch NPT (Model FE5) tapped hole; all three variations have a 1 inch NPT thread on the termination end. Other nipple alloys are available on special order. Bridges can be ordered with a protrusion ranging from 1 inch (2.5 cm) up to 19 inches (48 cm). All bridges without coupons are pressure rated for 150 psi (1,000 kPa) and tested to 300 psi.(2,000kPa). A high pressure version designated as FEH is rated for 300 psi (2,000 kPa) and tested to 600 psi (4,000 kPa). Bridges with coupons are rated to 25 psi. (173 kPa). Temperature rating on all designs is 210°F (98°C)
For intermittent readings, the reference electrode is simply pressed into the bridge. In this case, a single reference can be used with several bridges. When continuous readings are required, the reference electrode is threaded into the bridge. Reference elements available with this product are gelled copper/copper sulfate or gelled silver/silver chloride.
Our single piece Through Wall Reference Electrodes may be suitable in less demanding environments.
Element Selection Guide
EDI reference electrodes may be ordered with any of five different reference elements. The element selected depends upon the electrolyte in which the electrode is used.
Gelled copper/copper sulfate elements (EDI code CUG) are typically used in environments with less than 500 ppm chloride or other halides. They consist of high purity metallic copper immersed in a saturated CuSO4 solution containing a gelling agent. Use of these elements in electrolytes with higher halide levels or in electrolytes with any sulfides present will contaminate the element causing its reference potential to drift. Because of their widespread use, Cu/CuSO4 electrodes are the ones upon which many cathodic protection criteria are based. Cu/CuSO4 elements are available in all EDI product groups except Concrete Products.
Gelled silver/silver chloride elements (EDI code AGG) can be used in any environment which does not contain sulfides. They consist of 99.99% pure silver coated with silver chloride and immersed in a saturated potassium chloride solution containing a gelling agent. The reference potential of Ag/AgCl/sat. KCl elements is 105 mV negative to that of a saturated Cu/CuSO4 reference electrode. Ag/AgCl/sat. KCl elements are available in all EDI product groups.
Dry silver/silver chloride elements (EDI code AGD) are most commonly used in clean full strength seawater where the electrolyte comes into direct contact with the element. Like the gelled Ag/AgCl elements, they are adversely affected by sulfides. The reference potential of dry Ag/AgCl elements immersed in full strength seawater is 70 mV negative to that of a saturated Cu/CuSO4 reference electrode. As the ambient chloride level decreases, as would be the case when used in brackish water, the reference potential becomes less positive. Dry Ag/AgCl elements are only available in our through-wall, immersion and tubesheet mounted reference electrodes.
Dry silver/silver chloride elements for concrete (EDI code AGC) is a variation of our standard dry Ag/AgCl element which has been adapted for encasement in a cement-based grout. The reference potential depends on the pore water chloride level of the concrete structure in which it is embedded. This element is only available in our Marine Concrete reference electrode, EDI Model CM-AGC.
Zinc elements (EDI code ZIN) consist of high purity metallic zinc rod. When these elements are used in our underground reference electrodes, the zinc element is encased in a gypsum-bentonite backfill. The zinc element is directly wetted by the electrolyte in our through-wall and immersion reference groups. Reference potential of a zinc element encapsulated in backfill is about 1,100 mV negative to that of a saturated Cu/CuSO4 reference electrode. The reference potential of zinc directly exposed to an electrolyte depends on the composition of the electrolyte.
For More Information
Complete Product Information is available for downloading as pdf files. Click on the link below to download.
Process Vessel Reference Electrode (Model FE) data sheet. Installation Instructions for Process Vessel Reference Electrode (Model FE)
EDI products may be purchased from any corrosion control products distributor or directly from EDI.
